The pulp is the innermost layer of your tooth. It contains blood vessels that keep your teeth vibrant and healthy. But if you sustain damage to the tooth, such as a blow to the face or chronic grinding, the vessels might form an obstruction.
If blood cannot flow as needed to the tooth pulp, it can become non-vital. While not always deemed a dental emergency, non-vital tooth pulp can face a higher risk of an infection. For this reason, your dentist will want to keep an eye on a non-vital tooth.
You might wonder about the symptoms and prognosis related to this dental concern. Read on to learn details about non-vital tooth pulp, including diagnosing and treating this condition.
Symptoms of Non-Vital Tooth Pulp
The tooth pulp is not visible to the naked eye. But if you suffer damage to its internal blood vessels, you might notice some signs of this concern.
Without healthy blood flow, the tooth might start to look dull or grey in color. Sometimes the tooth might hurt, though the severity of this oral pain might vary. But many people do not experience any noticeable symptoms if they have non-vital tooth pulp.
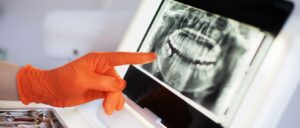
Primarily, a dentist can identify potential damage to a patient’s tooth pulp in a dental x-ray. The average dental patient should receive this routine imaging every year. If the dentist sees a blockage in a tooth’s pulp, they will want to perform a vitality test to confirm the diagnosis.
How a Dentist Tests Tooth Pulp Vitality
Dentists commonly test tooth pulp vitality through thermal testing. They will apply a cold stimulus to the affected tooth as well as several other spots in your mouth as controlled variables. Though the test triggers sensation within your mouth, you should only feel a slight discomfort that will fade upon the removal of the stimulus.
The dentist will monitor the speed of your reaction and degree of sensation during this test. If you have a slower reaction time or have less feeling from the stimulus, then the tooth pulp might be non-vital.
Prognosis for Non-Vital Tooth Pulp
Patients with non-vital tooth pulp do not always need further treatment from their dentist. If you have no other symptoms, your dentist will want to monitor this tooth because it can be in greater danger of infections or other dental complications.
But if you do feel pain in the tooth, it might already be infected. In this case, a dentist may need to perform root canal therapy to clear out bacteria in this part of the tooth and prevent further damage.
Some patients might want to address the dental discoloration that can develop in a non-vital tooth. The dentist can suggest dental bonding or veneers that can make the tooth look bright in your smile once more. Find dental solutions that suit your oral health needs by calling your dentist today.